Pulling a Box on a Horizontal Surface. Projectile motion part 1 This is the currently selected item.
Static and Kinetic Friction on an Inclined Plane.
. To solve projectile motion problems perform the following steps. Time for a given motion diagram. For this problem use the PhET simulation Projectile Motion.
Introductory Physics I PHYS 11A Description. Determine a coordinate system. Start the simulation by selecting the option labeled Intro.
Created by Sal Khan. Projectile Motion Tutorial Learning Goal 276231 -842257 -110026. Projectile Motion Tutorial Learning Goal.
In other words we will use one set of equations to describe the horizontal motion of the lime and another set of equations to describe the vertical motion of the lime. Now in this unit we will apply both. One unit of time elapses between consecutive dots in the motion diagram.
Study guide Getting Started on MasteringPhysics Introduction to Projectile Motion - Formulas and Equations Kinematics In One Dimension - Distance Velocity and Acceleration - Physics Practice Problems Python Tutorial - Python for Beginners Full CourseProblem 1461 Lesson 18 Mastering Physics Solution Inside the mind of a master procrastinator. In Unit 1 of the Physics Classroom Tutorial we learned a variety of means to describe the 1-dimensional motion of objects. It explains how to calculate the maximum height if a ball i.
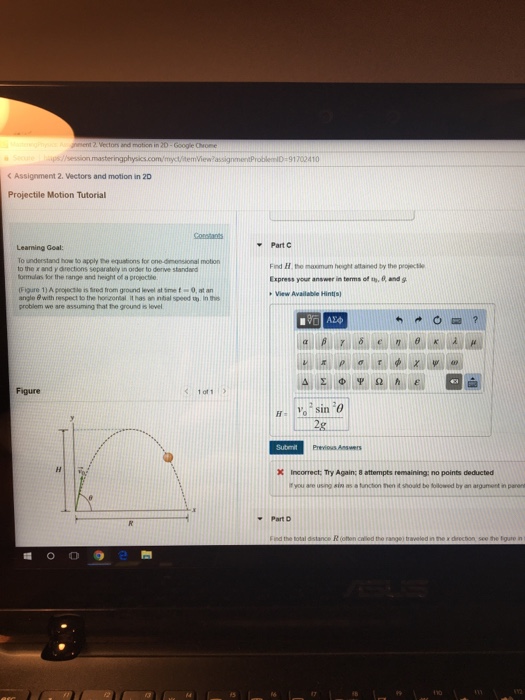
Find the time of flight from the y-motion 3. If v is the initial velocity g acceleration due to gravity and H maximum height in meters θ angle of the initial velocity from the horizontal plane radians or degrees. Consider the x and y motion separately.
Authored by Aaron Titus a well-known and respected. This turns a single difficult 2D problem into two simpler 1D problems. Projectile motion is the motion of an object through the air that is subject only to the acceleration of gravity.
Inclined Plane with Friction Two Masses and a Pulley. Graphing applet Constants Periodic Table For the motion diagram given sketch the shape of the corresponding motion graphs in Parts A to D. A cannon on a hill that fires horizontally ie.
The second half of the. It will help students visualize an objects motion in the x and y directions separately which is key to solving projectile motion problems. A projectile is fired from ground level at time horizontal.
Projectile motion is the motion experienced by an object in the air only under the influence of gravity. Now the cannon is pointed straight up and fired. Use the indicated coordinate system.
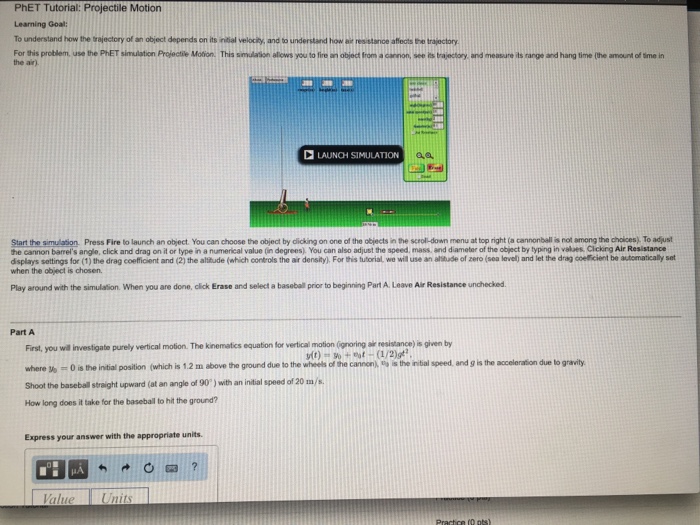
This simulation allows you to fire an object from a cannon see its trajectory and measure its height range and hang time the amount of time in the air. To understand projectile motion by considering horizontal constant velocity motion and vertical constant acceleration motion independently. Using the equations of motion to figure out things about falling objects.
Dont have an account. Find the x-position at the end of the flight - this is the range. In Unit 2 of the Physics Classroom Tutorial we learned how Newtons laws help to explain the motion and specifically the changes in the state of motion of objects that are either at rest or moving in 1-dimension.
HW 3_ 2D Motion and Projectiles Mastering Physics Answers. Now we will try to explain motion in two dimensions that is exactly called projectile motion. Mastering Physics Ph ET Tutorial Projectile Motion.
B Which of the paths would the cannonball most likely follow if the cannon barrel is horizontal. Then resolve the position andor velocity of the object in the horizontal and vertical components. This physics video tutorial provides projectile motion practice problems and plenty of examples.
The range of the projectile is dependent on the initial velocity of the object. A projectile is fired from ground level at time at an angle with respect to the horizontal. Some examples of Projectile Motion are Football A baseball.
The maximum height of. Up to 24 cash back Mastering Plwsics 21 - Projectile Moäon A cannon is fired from the top of a cliff as shown in the figure. In this problem we are assuming that the ground is level.
We can have different types of projectile type. Projectile motion refers to the motion of unpowered objects called projectiles such as balls or stones moving near the surface of the earth under the influence of the earths gravity alone. Projectile motion part 1 Transcript.
A projectile that is launched into the air near the surface of the Earths and moves along a curved path or in other words a parabolic path under the action of gravity assuming the air resistance is negligible. Constants Periodic Table Learning Goal. Projectile refers to an object that is in flight after being thrown or projected.
Old videos on projectile motion. It has an initial speed. Graph x and y components of position and velocity vs.
Projectile Motion Illustration This animation was designed to help beginners form correct conceptual understanding of projectile motion. If you remember these steps you can deal with many variants of the basic problem such as. Students use the PhET simulation Projectile Motion to understand how the trajectory of an object depends on its initial velocity and.
PROJECTILE MOTION We see one dimensional motion in previous topics. To understand how the trajectory of an object depends on its initial velocity and to understand how air resistance affects the trajectory. Take Has the height of the cliff a.
Exploring Projectile Motion Concepts. In this type of motion gravity is the only factor acting on our objects. Boat Crossing a River.
Students use the PhET simulation Projectile Motion to understand how the trajectory of an object depends on its initial velocity and to understand how air resistance affects the trajectory. Equations of motion therefore can be applied separately in X-axis and Y-axis to find the unknown parameters. Press the red Fire icon to launch an object.
To understand how to apply the equations for one-dimensional motion to the x and y directions separately in order to derive standard formulas for the range and height of a projectile. Ignore drag air friction for this question. Projectile motion part 2 Projectile motion part 3.
For example you throw the ball straight upward or you kick a ball and give it a speed at an angle to. One of the easiest ways to deal with 2D projectile motion is to just analyze the motion in each direction separately. In a projectile motion the only acceleration acting is in the vertical direction which is acceleration due to gravity g.
It has an initial speed at an angle with respect to the.

Answer Correct Projectile Motion Tutorial Learning Goal Understand How To Apply Course Hero
Solved 1702410 Assignment 2 Vectors And Motion In 2d Chegg Com

Mastering Physics Ph Et Tutorial Projectile Motion Phys 11a Studocu
Solved Phet Tutorial Projectile Motion Learning Goal To Chegg Com

Mastering Physics 3 Pdf Trajectory Euclidean Vector

55315748 14 Masteringphysics Assignment Print View Projectile Motion Tutorial Learning Goal Understand How To Apply The Equations For 1 Dimensional Course Hero

Chapter 3 Mastering Physics Introduction To Projectile Motion Learning Goal To Understand The Basic Concepts Of Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Course Hero
0 comments
Post a Comment